Also known as
Varicella-Zoster virus
Description
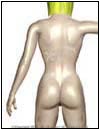 Normal |
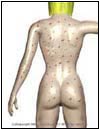 Abnormal |
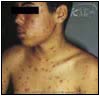 Abormal |
This is an infectious disease caused by the varicella virus. It is very contagious, spread by inhaling infected droplets. Some cases do occur totally without symptoms. The reactivation of the varicella virus many years later causes a disease called Shingles (explained in a different section).
Symptoms
- Rash characteristics:
-
- Begins as red, raised lesions
- Lesions then blister, fill with pus, burst, and scab over
- Most prominent on face, scalp, and trunk; less prominent but present on arms and legs
- Itching — can be severe
- Fever
- Malaise
How the diagnosis is made
- Usually evident by history and appearance to the doctor
- If unclear diagnosis —
– Tzanck smear of base of blister
Treatment
- Uncomplicated cases (majority) require symptomatic relief only:
-
- Keep skin clean
- Calamine lotion for itching
- Colloidal oatmeal baths for itching
- Antihistamines — over the counter Benadryl or prescription Zyrtec are good choices.
- Tylenol for fevers
- Isolate infected individuals from others who have not had Chicken Pox.
- Complicated cases:
- Anti-viral therapy such as Acyclovir or Famvir by mouth
-
- Immune compromised (such as HIV Infection) may need intravenous Acyclovir.
Complications
- Rash becomes secondarily infected (Cellulitis)
- Erysipelas
- Epiglottitis
- Scarlet fever
- Meningitis
Prevention
- There is now a vaccine against Chicken Pox that is recommended for anyone over 12 months of age who has not had the disease, and who does not have immune titers against it (the latter checked to determine if the case was without symptoms).
Similar Conditions
Miscellaneous
- Special Dangers
– Children — taking aspirin with chicken pox can lead to Reye’s syndrome, a severe disease that may result in brain damage and death. Children should never take aspirin if they have chicken pox. They should also not take aspirin for other diseases unless specifically directed to by a doctor. Tylenol and Ibuprofen are usually safe for children, but you should always check with your doctor. Always check what medications are safe when dealing with infants. Adults are much more likely to develop Pneumonia as a complication. In addition, patients with HIV Infection or immune system deficiencies are at even higher risk of Pneumonia. If you are pregnant and never had chicken pox, avoid contact with those with an active virus.
