|
|
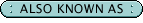 |
Inhalation of a foreign object; obstructed airway
|
 |
- A condition in which a foreign object is inhaled and lodged into the lower respiratory tract, via the mouth or nose, causing respiratory problems.
- It usually occurs in children who are between 6 months and 3 years of age.
- It occurs in boys twice as often as girls.
|
 |
- Aspiration may cause only minimal initial symptoms
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Harsh sound on inhalation
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
|
 |
- A peanut is the most common aspirated foreign object.
- Hot dogs, balloons, small toys, buttons, beads, coins, marbles, pins, screws, rocks, and anything else small enough for children to put in their mouth or nose.
|
 |
- Choking (object in airway) episode in only 50 - 80 % of cases
- Symptoms such as coughing, wheezing. But initial symptoms can be minimal until a lung infection presents.
- Pneumonia that does not respond to
antibiotics treatment
- Locally diminished or absent breath sounds in 50 % of cases
- Increased heart and respiration rate (i.e., number of
breaths per minute)
- Chest X-ray, inspiratory and expiratory X-ray: These may show air trapping, mediastinal shift, atelectasis, or lung infection.
- Fluoroscopy
- Rigid bronchoscopy for definitive diagnosis
|
 |
- Administering oxygen
- Rigid bronchoscopy to remove the object
- Antibiotics
- Chest physiotherapy after endoscopy
|
 |
- Call 911 immediately for emergency medical assistance. If you think your child has aspirated, he or she needs emergency treatment.
|
 |
- Do not leave your small child alone.
- Keep the small objects from your child.
- Do not force feed your child during crying or rapid breathing.
|
| | |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
under which this service is provided to you. Read our
.
Copyright © 2002 - 2003 eCureMe, Inc All right reserved.
|
 |
|
 |
|
|

