|
|
 |
Inflammation of
lung pleura
|
 |
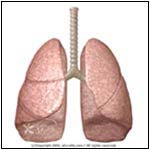
Normal |
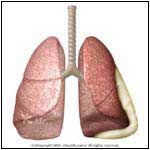
Abnormal |
|
|
- The Pleura is a sac surrounding the lungs. It consists of two layers, one covering the lung (visceral), while the other covers the inside of the chest wall or rib cage (parietal). Between the two layers is a space in which a small amount of fluid circulates to lubricate the two surfaces as they slide over one another during breathing.
- Pleurisy refers to the inflammation (irritation, swelling, stickiness) of the pleura. Pleurisy is not a disease, but a symptom of another condition (e.g., virus or bacterial infection).
- Inflammation of the pleura can lead to fluid build up (between the two layers) known as pleural effusion. During inflammation, sticky, fibrous material accumulates over the pleural surfaces, resulting in the layers rubbing against (friction rub) each other during breathing, and causing chest pain. Sometimes the inflammation is dry (i.e., dry pleurisy).
|
 |
- Fever
- Cough
- Chills
- Shortness of breath
- Weight loss
- Poor appetite
- Sharp chest pain with breathing. Pain can limit the movement on the side of the chest with pleurisy.
- Rapid shallow breaths
- Inability to take a deep breath due to chest pain
|
 |
- Symptoms
- Medications
- Illnesses
- Surgeries
- Allergies
- Occupation
- Travel
- Habits
- Body temperature may be elevated
- Rapid respiration
- Normal chest expansion during respiration is affected.
- Listening to the chest with a stethoscope, the doctor will hear the friction rub (i.e., creaky, coarse, rubbing sound).
- The heart sound and breath sounds
may be muffled due to presence of effusion.
- Blood tests may show evidence of infection -- elevated number of white blood cells and ESR.
- Blood may show evidence of cancer -- elevation of CA-125 (Ovarian Cancer), CA-19-9 (Pancreatic Cancer and others)
- Blood may show organ failure:
- High BUN/Creatinine -- Kidney failure
- High liver or pancreatic enzymes
- Low oxygen levels
- Chest X-Ray --
Pneumonia, asbestos
- CAT scan (using computers) and Ultrasound (using sound) can show fluid or effusion.
- Thoracentesis -- done by inserting a needle into the pleura. The removed effusion can then be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
|
 | |
|
 |
- Treat underlying disorder
- Rest
- Oxygen, if levels are low
- Aspirin and other NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen, Indocin, etc.) are effective in reducing the inflammation, fever, and pain.
- Painkillers such as codeine can help.
- In severe pain, a nerve block is performed using a numbing agent (e.g., Xylocaine) that is injected into the nerves between the ribs for temporary relief of pain.
- Therapeutic Thoracentesis is done to remove the effusion, which helps breathing.
|
 |
-
Contact a physician immediately. Call 911 if you have high fever, pain, or difficulty breathing.
|
| | |
If you want your friend to read or know about this article, Click here
 |
|
|

