|
|
 |
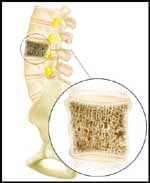
Normal |
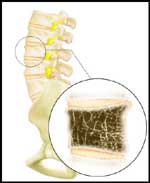
Abnormal |
|
- Osteoporosis is a disorder of the bone in which the bone literally becomes porous. Put simply, the bone loses substance and instead of staying solid, it develops the consistency of a dry sponge (i.e., with many areas that have tiny holes). These bones are brittle and are more likely to break or collapse.
- The most significant areas affected are the spine and hips. When the spine is affected, compression fractions occur. Compression Fractures
take place when the bones of the spine collapse upon themselves (patients often "shrink" in size). The neck of the femur (which is part of the hip) may break or collapse upon itself, as well resulting in Hip Fracture. Hip Fractures are very serious in elderly individuals and can lead to disability and even death in some cases.
|
 |
- Often none
- Back pain
- Loss of height
|
 |
- X-Rays of spine, hip and other parts of the body may show demineralization
- Bone density test (that evaluates the hip and spine) should be performed on all those at risk.
- Blood tests, which should be checked, include serum Calcium, phosphate, Alkaline phosphatase
and TSH. PTH or serum Protein Electrophoresis should be checked if indicated.
|
 | |
|
 |
- Walking and weight bearing exercises
- Calcium replacement-typical 1500mg of elemental Calcium if using Calcium carbonate (e.g., TUMS) or 500 mg of elemental Calcium if using Calcium citrate
- Vitamin D -- 400 to 800 i.u./day
- Hormone replacement in women e.g., estrogen such as Premarin
- Raloxifene can be used in those who cannot tolerate hormone replacement and in those with a history of Breast Cancer
- Testosterone in men with decreased androgen levels
- Bisphosphonates -- such as Alendronate (Fosamax) are effective treatment for osteoporosis. It can cause severe irritation to the esophagus and must be taken on an empty stomach with a large glass of water (and you may not lie down for 30 minutes afterward). A newer bisphosphonate called Actonel (Risedronate Sodium) does not have esophageal/gastrointestinal side effects of Fosamax
- Miacalcin --
this is a nasal spray form of the hormone Calcitonin.
- Calcium and vitamin D alone will not prevent osteoporosis
|
| | |
If you want your friend to read or know about this article, Click here
 |
|
|

